Overview
 Morton’s neuroma, also called Morton’s metatarsalgia, Morton’s disease, Morton’s neuralgia, Morton metatarsalgia, Morton nerve entrapment, plantar neuroma, or intermetatarsal neuroma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of nerve tissue (neuroma) that develops in the foot, usually between the third and fourth toes (an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the third and fourth intermetatarsal spaces). It is a common, painful condition.
Morton’s neuroma, also called Morton’s metatarsalgia, Morton’s disease, Morton’s neuralgia, Morton metatarsalgia, Morton nerve entrapment, plantar neuroma, or intermetatarsal neuroma is a benign (non-cancerous) growth of nerve tissue (neuroma) that develops in the foot, usually between the third and fourth toes (an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the third and fourth intermetatarsal spaces). It is a common, painful condition.
Causes
Although the exact cause for this condition is unclear, a number of factors can contribute to the formation of a neuroma. Biomechanical deformities, such as a high-arched foot or a flat foot, can lead to the formation of a neuroma. These foot types bring on instability around the toe joints, leading to the development of the condition. Trauma can cause damage to the nerve, resulting in inflammation or swelling of the nerve. Improper footwear that causes the toes to be squeezed together is problematic. Avoid high-heeled shoes higher than two inches. Shoes at this height can increase pressure on the forefoot area. Repeated stress, common to many occupations, can create or aggravate a neuroma.
Symptoms
The most common presenting complaints include pain and dysesthesias in the forefoot and corresponding toes adjacent to the neuroma. Pain is described as sharp and burning, and it may be associated with cramping. Numbness often is observed in the toes adjacent to the neuroma and seems to occur along with episodes of pain. Pain typically is intermittent, as episodes often occur for minutes to hours at a time and have long intervals (ie, weeks to months) between a single or small group of multiple attacks. Some patients describe the sensation as “walking on a marble.” Massage of the affected area offers significant relief. Narrow tight high-heeled shoes aggravate the symptoms. Night pain is reported but is rare.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of interdigital neuroma is usually made by physical examination and review of the patient’s medical history.MRI ad High Definition Ultrasound examination may be useful to confirm the diagnoses however they may still not be 100% reliable. The commonest reason for this is de to natural substances present in between the metatarsal heads and between the fat pad and the intermetatarsal ligament. These natural substances i.e. bursa, fat, capsular thickening and even bony growths, can all be a factor in the impingement process and may need to be surgically cleared.
Non Surgical Treatment
The good news is that the pain can often be relieved fairly easily with the right softer styled orthotic (even in those cases where there is concurrent plantar plate tears and capsulitis!), but its important to remeber that even if your no longer in pain, there is no magic cure to speeding up the healing process so one must take care of their feet for 6-12 weeks. As a rule of thumb a neuroma should always be treated conservatively where possible. This means icing and resting the area, trying to remove the causative factors, and providing postural control and support via metatarsal domes or, if needed, specialised pre-made or custom made orthotics.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery to remove the neuroma may be recommended if more conservative treatment does not solve the problem. While surgery usually relieves or completely removes the symptoms, it often leaves a permanent numb feeling at the site of the neuroma.
 Overview
Overview Symptoms
Symptoms

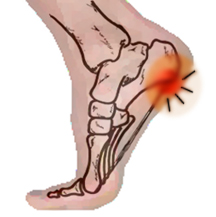

 Achilles tendinitis is an inflammation (swelling) of the tendon, which usually occurs as a result of overuse injury. Basketball players are the most susceptible to Achilles tendinitis because of the frequent jumping. Any activity requiring a constant pushing off the foot, such as running or dancing, may result in swelling of the tendon.
Achilles tendinitis is an inflammation (swelling) of the tendon, which usually occurs as a result of overuse injury. Basketball players are the most susceptible to Achilles tendinitis because of the frequent jumping. Any activity requiring a constant pushing off the foot, such as running or dancing, may result in swelling of the tendon.








You must be logged in to post a comment.